n. pl. hy·per·bo·las or hy·per·bo·lae (-lē) A plane curve having two branches, formed by the intersection of a plane with both halves of a right circular cone at an angle parallel to the axis of the cone. It is the locus of points for which the difference of the distances from two given points is a constant. [New Latin, from Greek huperbolē, a throwing beyond, excess (from the relationship between the line joining the vertices of a conic and the line through its focus and parallel to its directrix); see HYPERBOLE.] 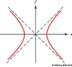 (click for a larger image) hyperbolaThe equation of this hyperbola is x2 - y2 = 1. |
The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition copyright ©2022 by HarperCollins Publishers. All rights reserved.







